In the circuit shown, if $v(t)=2 \sin(1000\: t)$ volts, $R=1\:k \Omega$ and $C=1\:\mu F,$ then the steady-state current $i(t)$, milliamperes (mA), is
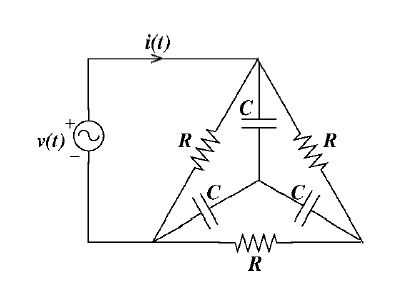
- $\sin(1000\: t)+ \cos(1000\: t)$
- $2 \sin(1000\: t) +2 \cos(1000\: t)$
- $3 \sin(1000\: t) + \cos(1000\: t)$
- $\sin(1000\: t) +3 \cos(1000\: t)$