Consider the CMOS circuit shown, where the gate voltage $V_{G}$ of the $\text{n-MOSFET}$ is increased from zero, while the gate voltage of the $\text{p-MOSFET}$ is kept constant at $3 \mathrm{~V}$. Assume that, for both transistors, the magnitude of the threshold voltage is $1 \mathrm{~V}$ and the product of the transconductance parameter and the $\text{(W/L)}$ ratio, i.e. the quantity $\mu C_{o r}(\mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{L})$, is $1 \mathrm{~mA} \cdot \mathrm{V}^{-2}$.
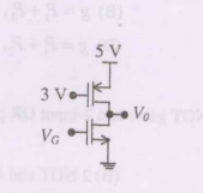
For small increase in $V_{G}$ beyond $1 \mathrm{~V}$, which of the following gives the correct description of the region of operation of each MOSFET ?
- Both the MOSFETs are in saturation region
- Both the MOSFETs are in triode region
- $\text{n-MOSFET}$ is in triode and $\text{p-MOSFET}$ is in saturation region
- $\text{n-MOSFET}$ is in saturation and $\text{p-MOSFET}$ is in triode region