An optical fiber consists of a cylindrical dielectric rod of refractive index $\mathrm{n}^{1}$, surrounded by another dielectric of refractive index $n^{2}$, where $n^{2} < n^{1},$ as shown in the following figure. If a ray is incident from air at an angle $i$ to the axis, then it undergoes total internal reflection at the interface $AB$ if
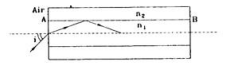
- $i \geq \sin ^{-1} \sqrt{n_{1}^{2}-n_{2}^{2}}$
- $i<\sin ^{-1} \sqrt{n_{1}-n_{2}}$
- $i \geq \sin ^{-1} \sqrt{n_{1}^{2}-n_{2}^{2}}$
- $i=\sin ^{-1} \sqrt{n_{1}-n_{2}}$